|
|
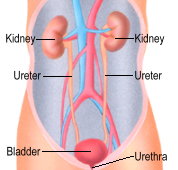
The Urinary
Tract |
Cystitis is an infection
of the urinary bladder.
It occurs when bacteria
travel up the urethra
(the passage which the
urine passes from the
bladder to the outside),
infect the urine and
inflame the bladder
lining. It is the
most common type of
urinary tract infection,
particularly in women.
This is because of their
short urethra and its
positioning; the
urethra lies close to
the anus and vagina
which allows bacteria
from these areas to
easily migrate and
travel up the urethra
into the bladder.
There is always the
danger that the
infection may ascend via
the ureters into the
kidneys causing
pyelonephritis (kidney
infection).
|
Common Causes of
Cystitis |
|
►
|
|
Poor
toilet hygiene. In
female, wiping the
bottom from back to
front after passing
stool or urine brings bacteria
from the anal or
vagina to enter the
urethra.
|
|
|
► |
|
Obstruction of the
urethra which
prevent all of the
urine to be emptied
from the bladder.
The remaining urine
in the bladder
provides a bleeding
ground from
bacteria.
Causes of urethra
obstruction may be
due to narrowing
urethra or enlarge
prostate (in men).
|
|
|
► |
|
Inadequate emptying
of bladder may also
due to the effect of
some drugs (example,
antidepressants),
immobility, abnormal
bladder control and
constipation.
|
|
|
► |
|
Fail to observe
proper hygiene and
catheter care for
people who are using
urinary catheter.
|
|
|
►
|
|
Tight-fitting
clothes such as
underwear or pants,
which trap heat and
moisture, making the
genital area
conducive to
bacteria growth.
|
|
Return to Top
|
►
|
|
Frequent urge to
urinate with small
amount.
|
|
|
► |
|
Pain or burning
sensations during
urination.
|
|
|
► |
|
Concentrated, cloudy
and foul-smelling
urine because of the
presence of
bacteria.
|
|
|
► |
|
Discomfort or ache
in the lower abdomen
(above the pubic
bone) and lower
back.
|
|
|
►
|
|
May have blood
stains in the urine.
|
|
|
► |
|
Return to Top
|
Homecare Tips
and How to
Prevent Further
Attacks |
|
►
|
|
Drink sufficiently.
This can help to
flush out the
bacteria from the
bladder through
urination.
|
|
|
► |
|
Avoid foods or
drinks that can
irritate the
bladder. These
include coffee, soft
drinks with
caffeine, alcohol,
citrus juices and
spicy foods.
|
|
|
► |
|
Pass urine as soon
as the urge is felt.
Retaining urine in
the bladder allows
bacteria to thrive.
|
|
|
► |
|
When using a sitting toilet,
to facilitate a
complete emptying of
bladder, the correct
posture is to place
yourself backwards
on the toilet, so
you lean against the
wall. It is a
bad habit to sit on
the toilet, bent
forward and reading
while urinating.
|
|
|
►
|
|
Practice proper
toilet hygiene.
In female, after
passing stool or
urine, always wipe
from front to back
(urethra to anus),
to avoid carrying
bacteria from the
bowel to the
bladder.
|
|
|
► |
|
Wash the genital
area well before and
after sexual
intercourse.
|
|
|
► |
|
The woman should
urinate immediately
after intercourse to
wash away bacteria
that may have
entered the urethra.
|
|
|
► |
|
Women should change
their sanitary pads
frequently because
bacteria thrive in
blood.
|
|
|
►
|
|
Avoid tight-fitting
underwear or pants
which trap heat and
moisture. This
makes the genital
area conducive to
bacteria growth.
Wear cotton rather
than nylon
underwear.
|
|
|
► |
|
Do not use perfumed
soaps, talcum powder
or any type of
deodorant around the
genitals.
|
|
|
► |
|
Studies have shown
that cranberry juice
may decrease the
incident of urinary
tract infections.
It works by
preventing common
bacteria from
‘sticking’ to the
walls of the
bladder.
Consult your doctor
prior to taking
cranberry juice as
it can alter the
effectiveness of
some antibiotics.
|
|
Return to Top
|
►
|
|
Pain below the ribs
including the
abdomen may indicate
that the infection
has spread to the
kidneys. In
extreme cases, it
causes vomiting and
high fever. If
untreated, it may
cause permanently
damage to the
kidneys.
|
|
|
► |
|
People who
experience frequent
episodes of cystitis
should consult their
doctors for close
evaluation to
establish the
underlying problem.
|
|
Return to Top
|
|
|